We offer various micropositioners for electrophysiology setups. These range from manually controlled mechanical micromanipulators to closed-loop controlled x/y stages for microscopy with sub-micron precision.
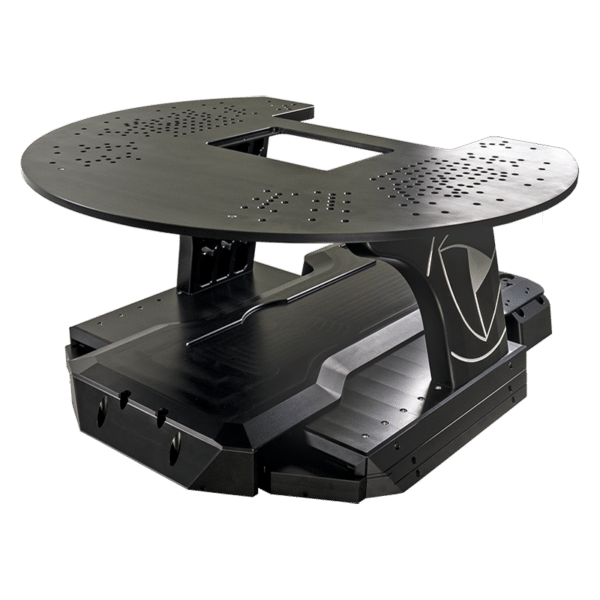
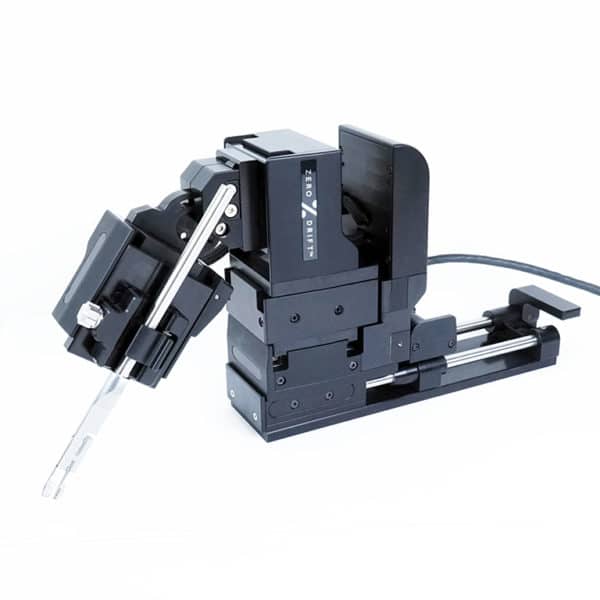
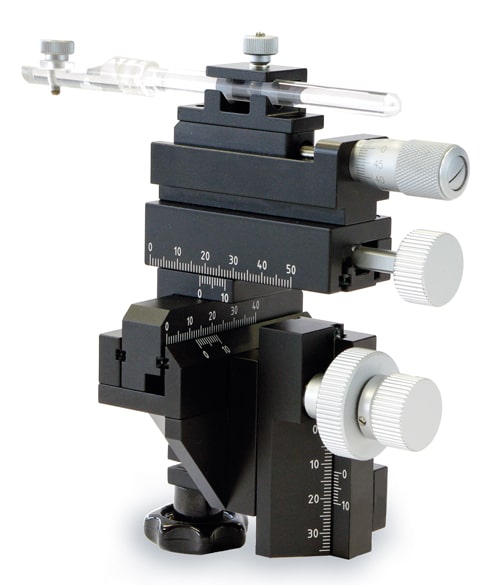
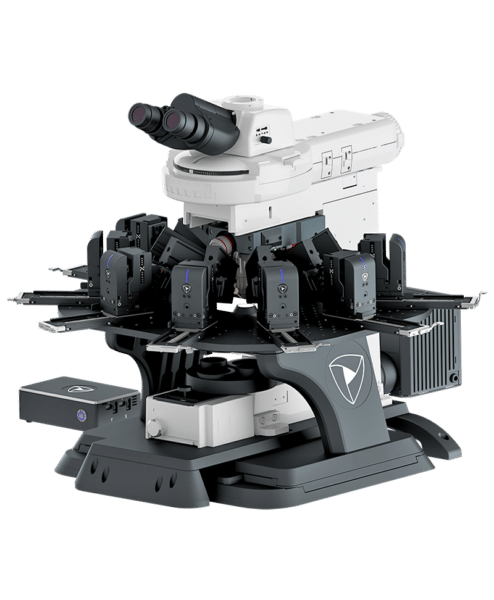

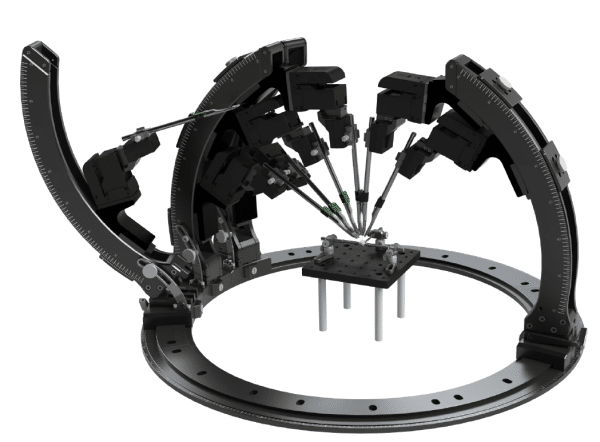





Micropositioners are precision devices used to manipulate electrodes or other tools in electrophysiological experiments. They allow for fine control over the positioning of these tools with micrometer-level accuracy.
Micropositioners are essential in electrophysiology because they provide the precision needed to place electrodes accurately on or within neurons or other cells. This accuracy is crucial for recording electrical activity without damaging the cells or tissues being studied.
The main types of micropositioners include manual, motorized, and hydraulic micropositioners. Manual micropositioners are adjusted by hand, motorized ones use electric motors for positioning, and hydraulic micropositioners use fluid pressure for movement.
Manual micropositioners are adjusted using screws or knobs that move the electrode holder in very small increments. The precision of these movements depends on the design and quality of the screws and the overall construction of the micropositioner.
Motorized micropositioners offer greater precision and repeatability compared to manual versions. They can be controlled remotely, allowing for automated adjustments and integration with computer-controlled experimental setups.
Important factors include the level of precision required, the type of movement control (manual, motorized, or hydraulic), compatibility with other laboratory equipment, ease of use, and the specific needs of your experimental setup.
By allowing precise placement of electrodes, micropositioners help ensure that the electrical signals being recorded come from the desired location. This precision reduces noise and artifact in the data, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
Challenges include maintaining stability during long experiments, ensuring precise and repeatable movements, avoiding damage to delicate tissues, and integrating the micropositioner with other laboratory equipment and software.
Yes, micropositioners are also used in other fields that require precise positioning, such as materials science, microelectronics, and neurophysiology. Their ability to manipulate tools with high precision makes them versatile instruments in many scientific and engineering disciplines.